Plastic Manufacturing Methods
Plastics are made into shapes in many ways:
 1. EXTRUSION
1. EXTRUSION
Hot molten plastic is squeezed through a nozzle to make long lengths of special shapes like pipes, spouting and wallboard joining strips. It is also used to make large thick sheets of plastic for fabrication.
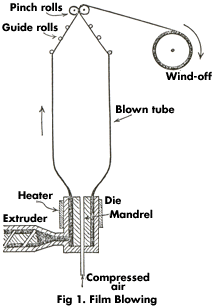
2. BLOW EXTRUSION (Fig 1)
This is used for making plastic films and bags. While it is still hot, an extruded tube is blown up like a balloon, with compressed air. This stretches the plastic and makes it thin. The balloon is made long enough to allow the plastic to cool. The end of the balloon is pinched together by rollers, to hold the air in and make it flat. The flat tube is then wound on to a big roll. You can see continuous rolls of plastic bags in a fruit shop.
3. INJECTION MOULDING
Hot molten plastic is squeezed into a mould to make lots of objects all the same. They can be very small like a washer or quite large, like a bowl or a clothes basket. Lots of everyday articles are made this way.
4. BLOW MOULDING (Fig 2)
A little bit of hot soft plastic is squeezed into the end of a mould. Compressed air is used to blow a big bubble inside the plastic. The plastic swells out like a balloon until it fills up the whole mould. Many bottles, toys and money boxes are made this way.

5. ROTATIONAL MOULDING
Plastic powder is scooped into a mould. The mould is rotated over a big gas burner. As the mould gets hot, the plastic melts and sticks to the mould. This method is used for making big hollow things like water tanks and barrels.
6. COMPRESSION MOULDING
This is used for thermoset resins. Dry powder is put in a mould which is squeezed and heated until the plastic is cured. This is used for making ashtrays, cups and plates, and some electrical switches.
7. REACTION INJECTION MOULDING
Two chemicals are mixed together and squirted into a mould. The chemicals react together. This is how they make car bumpers, some disposable cups and plates, and the meat trays you get from supermarkets.
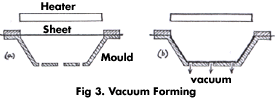
8. VACUUM FORMING ( Fig 3)
A sheet of plastic is clamped in a frame and heated until it is stretchy. Then it is sucked into a mould. This is how they make the inside of your refrigerator, bath and handbasin. It is also used to make a lot of packaging for cosmetics, chocolates, biscuits, some yoghurt containers and some disposable cups.
9. FABRICATION
Some thermoplastics are fabricated like sheetmetal. Sheets of plastic are cut to shape. They can be folded by heating a narrow line through the plastic. When it is soft, the sheet will bend along the heated line. Sheets can be joined together by glueing, or by welding. The join is heated with hot air and a thin filler rod is forced into the gap. These fabrication methods are used to make acrylic signs and displays, and industrial tanks and equipment. Our company, Calibre Plastics, uses fabricating methods to manufacture laboratory fume cupboards and exhaust fans.
Thin flexible plastic sheets are used for making folders, wallets, swimming pool liners, inflatable toys and raincoats. The seams are welded by ultrasonic vibration.
10. A Special Note About Styrene Foam.
Styrene foam is made in little pellets. To make blocks of styrene foam, or complicated shapes like a cycle helmet, they scoop lots of pellets into a mould and heat it with steam. The steam makes the pellets swell up and stick together. When you break a moulded block you can see how all the pellets have squashed into each other.

